Android Third Parties Note
Glide
「A fast and efficient image loading library for Android focused on smooth scrolling.」Reference: About Glide - Manual.
// usage sample
Glide.with(context).load(url).into(imageView);
- Features of Glide:
- Memory management with disk & memory caching.
- Resource reusing by bitmap pooling.
- Efficient decoding with downsampling.
Caches in Glide help saving time of loading a resource. Glide checks multiple layers of caches before really starting a new request for an image. 👇
Specifically, it checks if the resource is on memory (active resources, and memory cache), then it checks if the resource is on disk (resource, and data) asynchronously. Then if all four places are failed to provide resource, then Glide really starts to retrieve the original resource from given source. See Caching - Manual.
// Engine.java
public <R> LoadStatus load(..) {
..
EngineResource<?> memoryResource;
synchronized (this) {
//If the resource is on memory?
//1. Active resources - Is this image displayed in another View right now?
//2. Memory cache (LRU) - Was this image recently loaded and still in memory?
memoryResource = loadFromMemory(key, isMemoryCacheable, startTime);
if (memoryResource == null) {
//If the resource is on disk?
//3. Resource (LRU) - Has this image been decoded, transformed, and written to the disk cache before?
//4. Data (LRU) - Was the data this image was obtained from written to the disk cache before?
//5. Source - load the original resource from given source data.
return waitForExistingOrStartNewJob(..)
}
}
..
}
@Nullable
private EngineResource<?> loadFromMemory(
EngineKey key, boolean isMemoryCacheable, long startTime) {
..
//1. Active resources
EngineResource<?> active = loadFromActiveResources(key);
..
//2. Memory cache (LRU)
EngineResource<?> cached = loadFromCache(key);
..
}
Technically, 1) active resources uses a HashMap<Key, ResourceWeakReference> , 2) memory cache is a LinkedHashMap<> implemented in public class LruResourceCache extends LruCache<Key, Resource<?>> implements MemoryCache .
While checking on disk is wrapped in a DecodeJob , executed by EngineJob, started by Engine. In DecodeJob , the checking is delivered through Resource_Cache → Data_Cache → Source → Finish.
// DecodeJob.java
private void runGenerators() {
..
stage = getNextStage(stage);
currentGenerator = getNextGenerator();
..
}
private Stage getNextStage(Stage current) {
switch (current) {
case INITIALIZE:
..
case RESOURCE_CACHE:
..
case DATA_CACHE:
..
case SOURCE:
case FINISHED:
..
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized run reason: " + runReason);
}
}
private DataFetcherGenerator getNextGenerator() {
switch (stage) {
case RESOURCE_CACHE:
return new ResourceCacheGenerator(decodeHelper, this);
case DATA_CACHE:
return new DataCacheGenerator(decodeHelper, this);
case SOURCE:
return new SourceGenerator(decodeHelper, this);
case FINISHED:
return null;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized stage: " + stage);
}
}
Glide manages caches (memory & disk) in LRU and automatically evicts contents when needed by responding ComponentCallbacks2 . See Caching - Resource Management, Manual.
// Glide.java
public class Glide implements ComponentCallbacks2 {
@Override
public void onTrimMemory(int level) {
trimMemory(level);
}
}
How to invalidate caches in Glide?
See Caching - Cache Invalidation, Manual.
In practice, the best way to invalidate a cache file is to change your identifier when the content changes (url, uri, file path etc) when possible.
RxJava
How does observer get update from subscriber?
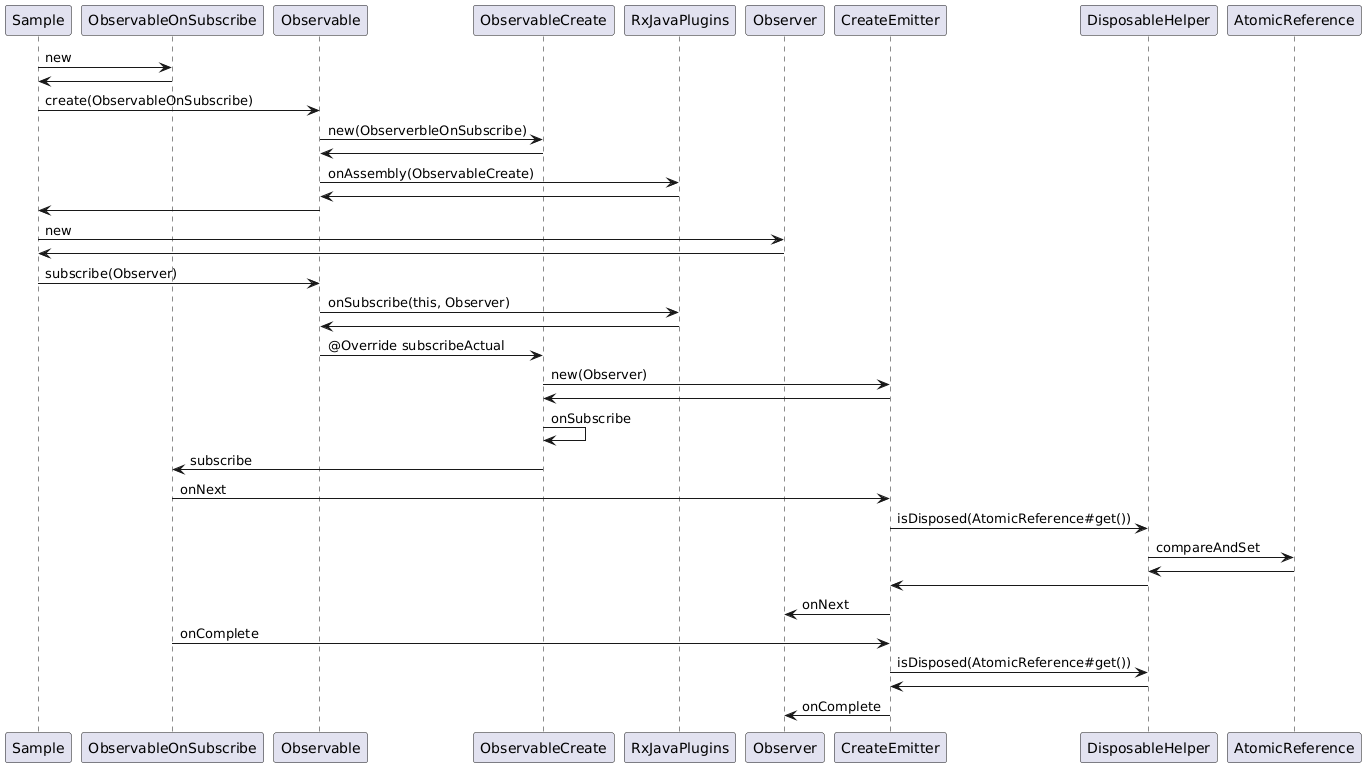
How does thread switch in RxJava?
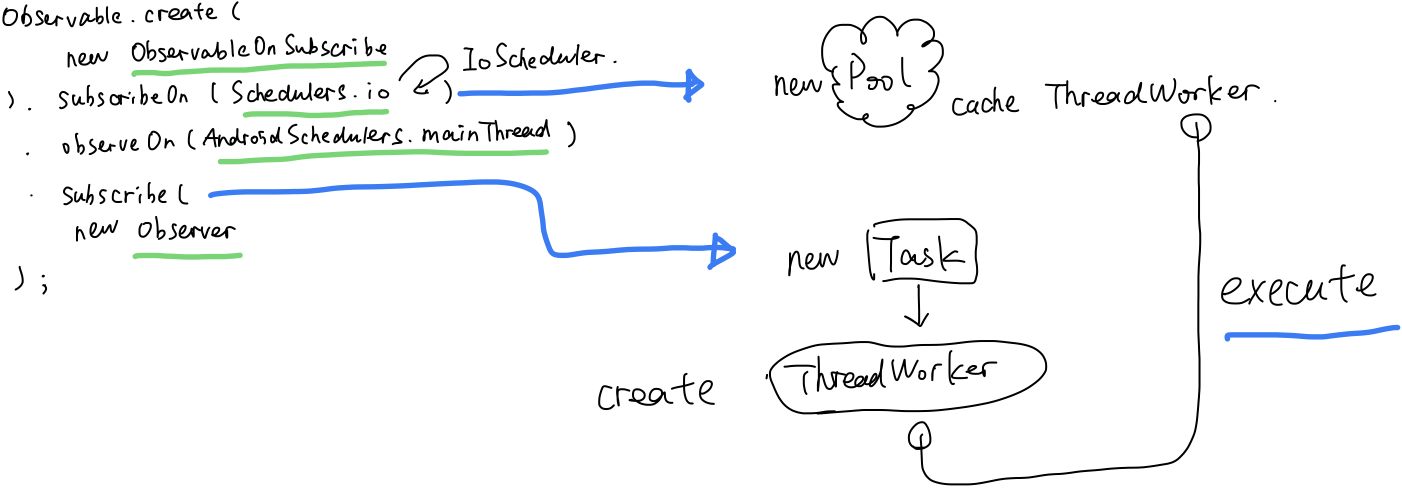
Reference: Android开源库源码分析 - RxJava的线程切换